Urinary Tract Infection
What is Urinary Tract Infection
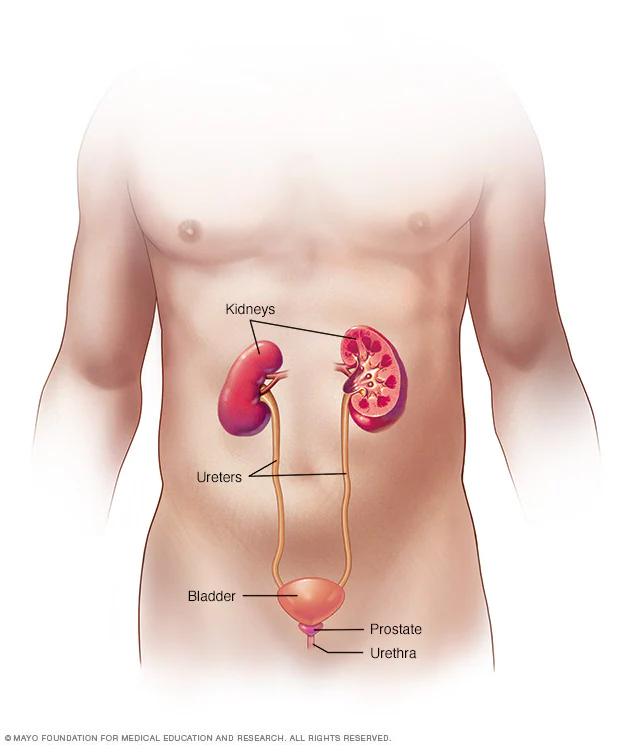
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. Typically, UTIs are caused by bacteria, especially Escherichia coli (E. coli), and they are more common in women due to their shorter urethra. As a result, a UTI can cause symptoms like painful urination, frequent urination, urinary urgency, and cloudy or bloody urine.
Causes
Poor Hygiene
Wiping from back to front after using the toilet can spread bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
Sexual Activity
Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra.
Weakened Immune System
Conditions like diabetes or HIV can impair the immune system, making it easier for infections to develop.
Pregnancy
Hormonal and anatomical changes during pregnancy increase the risk of UTIs.
Urinary Retention
Infrequent urination or not fully emptying the bladder increases the risk of bacterial growth.
Catheter Use
Using a urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
Anatomical Abnormalities
Certain birth defects or structural abnormalities in the urinary tract can make someone more prone to UTIs.
Treatment
Treatment for UTIs usually involves antibiotics to clear the infection. Specific treatments depend on the location and severity of the infection:
Antibiotics: A healthcare provider will prescribe antibiotics based on the type of bacteria causing the infection. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the infection from returning.
Pain relievers: Medications like phenazopyridine can help relieve discomfort associated with painful urination.
Increased fluid intake: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary system.
Cranberry supplements: Though their effectiveness is debated, cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent UTIs in some individuals.
For recurrent UTIs, preventive strategies might include long-term low-dose antibiotics, self-testing for infections, or lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors. Additionally, in rare cases, doctors may recommend surgery to correct anatomical issues that cause frequent infections.