What is hyperthermia treatment?
Hyperthermia is a treatment that involves raising the temperature of body tissues to as high as 113°F to damage and destroy cancer cells, with minimal impact on healthy tissues. Doctors use this technique, also called thermal therapy, thermal ablation, or thermotherapy, to enhance other cancer treatments like radiation and chemotherapy. By increasing blood flow to the tumor site, hyperthermia helps make cancer cells more sensitive to these treatments. It can also promote the release of heat-shock proteins, which aid in the destruction of cancer cells. Doctors often use this non-invasive approach with other therapies to improve outcomes and reduce side effects.
How hyperthermia treats cancer
Hyperthermia is typically used in conjunction with other cancer treatments. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated that when combined with therapies like radiation and chemotherapy, hyperthermia can help shrink tumors and increase the effectiveness of these treatments in destroying cancer cells. The heat from hyperthermia improves blood flow to the tumor, making it more susceptible to the effects of radiation and chemotherapy, and may even enhance the body’s immune response to cancer.
Benefits of Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia can enhance the effectiveness of other cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy, making tumors more responsive to these therapies and helping to shrink them more effectively.
How Hyperthermia is Administered
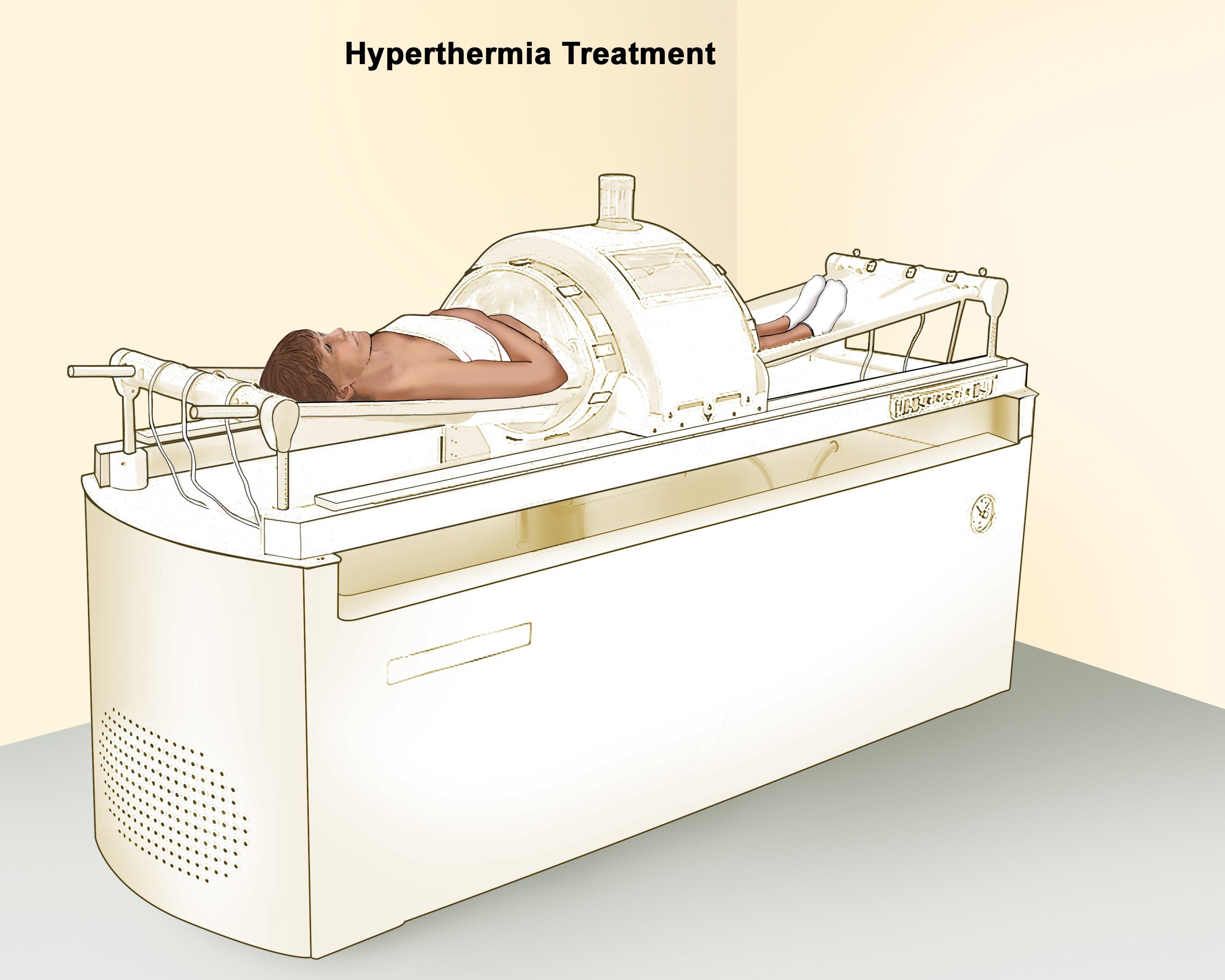
During hyperthermia treatment, the doctor first numbs the treatment area before inserting small probes with tiny thermometers into the tumor. These thermometers allow the doctor to closely monitor the temperature of the tumor and surrounding tissues. Technicians use imaging techniques like CT scans to position the probes accurately. They monitor precisely to heat the tumor to the optimal temperature for maximum effectiveness while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.

Drawbacks of Hyperthermia for Cancer Treatment
Although hyperthermia can be beneficial, it requires specialized equipment and expertise, which means it is not widely available. Additionally, it is still unclear whether hyperthermia directly contributes to increased survival rates for cancer patients.
Side Effects of Hyperthermia
Keeping the temperature below 111°F generally prevents hyperthermia from damaging healthy tissue. However, variations in tissue characteristics may cause localized higher temperatures, leading to burns, blisters, discomfort, or pain. Perfusion techniques, used to enhance blood flow during treatment, can result in swelling, blood clots, bleeding, and other damage to normal tissues, though most of these side effects resolve after treatment.
Whole-body hyperthermia can lead to more general side effects, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. In rare cases, more serious side effects like heart and blood vessel complications may occur.
Where to Get Hyperthermia Treatment
Only a small number of hospitals and cancer centers have the specialized equipment and trained doctors needed to administer hyperthermia. If you’re considering this treatment, consult with your doctor or contact local hospitals and cancer centers to see if they offer hyperthermia therapy.