An Advanced Diagnostic Tool for Detecting Prostate Cancer on a Cellular Level through Genomic Prostate Cancer Testing
We actively explore all available methods to detect cancer as early, accurately, and noninvasively as possible. As part of this innovative approach, we have incorporated Genomic Prostate Cancer Testing into our program, using this cutting-edge diagnostic tool when appropriate to provide personalized insights and improve detection accuracy.
Did you know that up to 1 in 4 men with negative biopsy results may still have prostate cancer? This is because traditional TRUS biopsies are highly limited, sampling less than 1% of the entire prostate gland. We recommend 3T Multi-Parametric MRI-guided biopsies due to their real-time 3D tumor visualization, which greatly enhances targeting accuracy and reduces invasiveness.
Now, with the addition of epigenetic analysis, we are able to offer even greater diagnostic precision—and provide peace of mind for our patients.
ConfirmMDx Genomic Analysis works at the DNA level to differentiate true-negative biopsies from missed hidden cancers. It identifies the “Field Effect,” an epigenetic change or “halo” around cancerous areas at the DNA level. This halo can exist even when cancer cells appear normal under a microscope or MRI. Standard microscopy and advanced mpMRI cannot detect these molecular changes. However, ConfirmMDx provides valuable insight into whether cancer is truly absent or hidden.
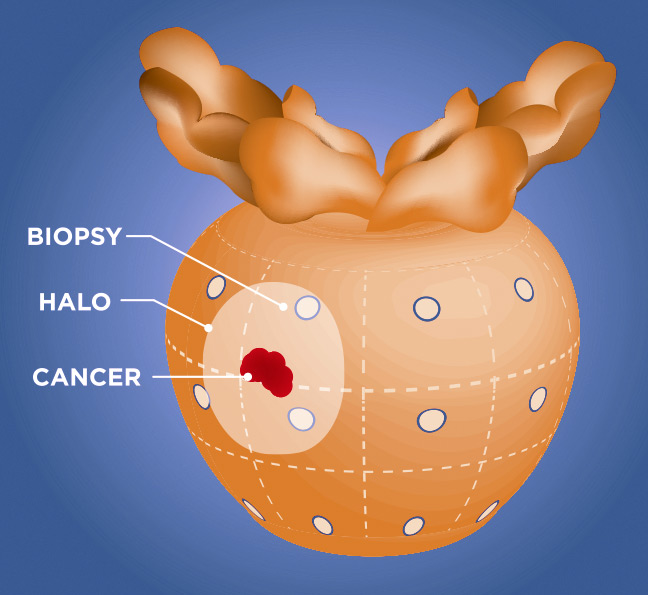

When we detect a halo, we perform additional laboratory analyses to build a detailed genomic profile and assess the patient’s risk level.
- Oncotype Dx – Oncotype Dx analyzes tissue samples after a prostate biopsy by evaluating the activity of specific cancer genes. It produces a Genomic Prostate Score that indicates the likelihood of cancer progression and spread if untreated. This analysis helps patients considering Active Surveillance or treatment make well-informed decisions.
- ProstaVysion – This test also uses biopsy tissue to analyze a sequence of genes to determine the genetic aggression of the cancer. By assessing the risk of future growth and spread, it provides valuable guidance, especially for patients considering Active Surveillance.
- Prolaris – Prolaris measures how quickly cancer cells divide to assess their aggressiveness instead of focusing on gene sequencing. This analysis helps patients with low-risk disease based on biopsy results by providing additional clarity. Doctors also use Prolaris after radical prostatectomy to evaluate the likelihood of cancer recurrence. It helps determine if additional treatments, like radiation or hormone therapy, are necessary after surgery.